Scheduling lists in GeMRTOS #
In GeMRTOS, each task is assigned to a scheduling list and one or more processors may serve that scheduling list. Processors may serve one or more scheduling lists, thereby allowing the predictability of partitioned scheduling with a flexible balance of processor loads. Scheduling overhead is reduced using a timer-tickless scheduler. Floating scheduling reduces the overhead for the highest priority tasks and isolates the design of the system from the number of processors of the hardware architecture. The generic feature allows partial configuring, global and partitioned scheduling. Hybrid partition scheduling are based on scheduling lists which allow assigning tasks and processors to scheduling the different subsystems of the application.
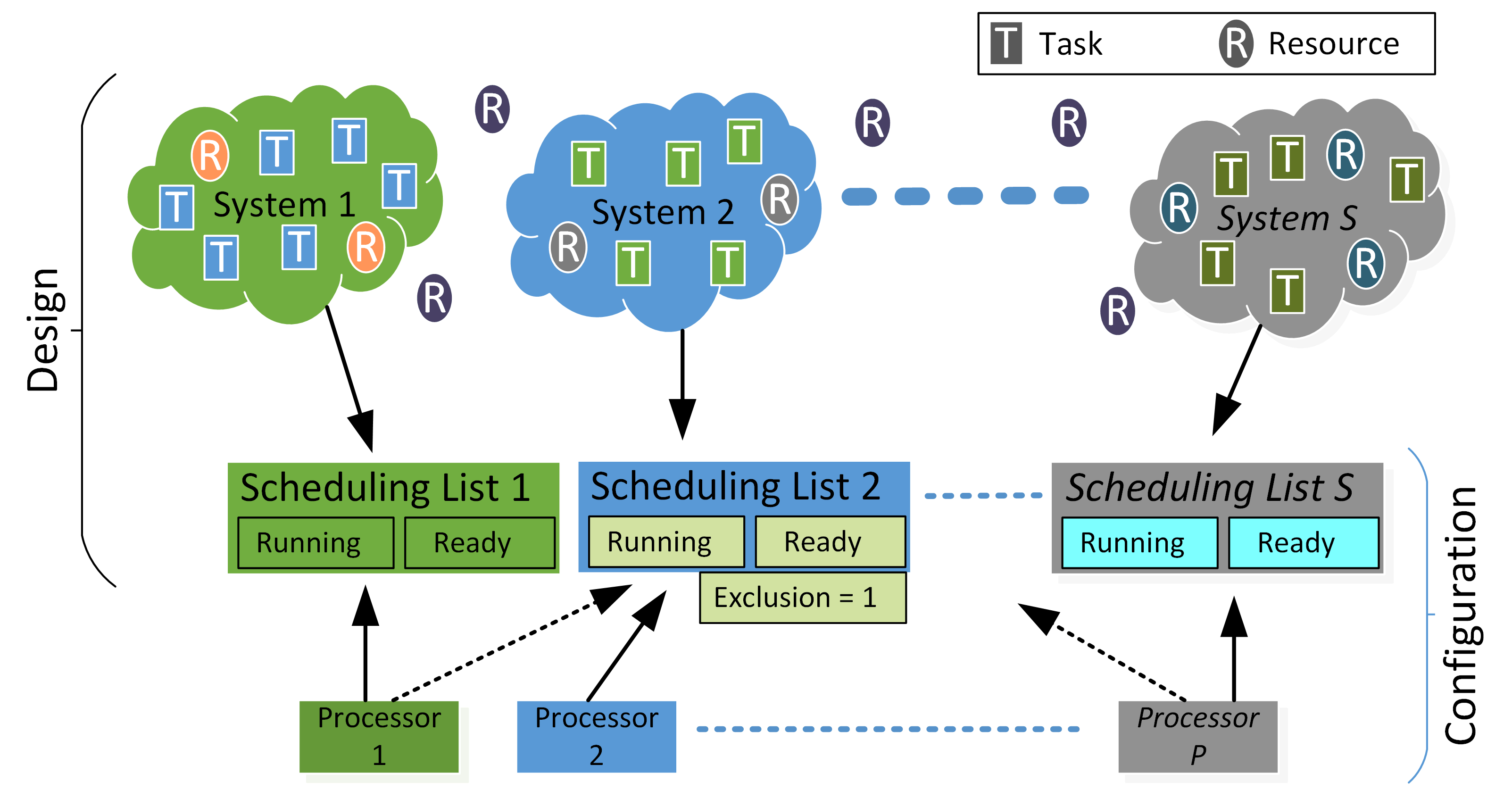
Resources may be shared among tasks from several scheduling lists, as shown in the figure. Each scheduling list may implement a different scheduling priority and task may be migrated from one scheduling list to another scheduling list during runtime. Processors may be assigned to several scheduling lists, and their assignment may change at any time during runtime
Types of GeMRTOS scheduling lists #
The following are the type of tasks in GeMRTOS, but more can be defined:
lcbtype
Enumerator GS_LCBType_UNSPECIFIED State UNLINKED for LIST
GS_LCBType_EDF The GS_LCBType_EDF scheduling list type implements the Earliest Deadline First (EDF) discipline among the tasks assigned to the scheduling list. In the EDF discipline, the earliest deadline, the highest priority. In order to maintain consistency, tasks that are assigned to an EDF scheduled list should be of the periodic type, with the deadline taken into account starting from the release time.
- Remarks
- GS_LCBType_EDF
GS_LCBType_FP The GS_LCBType_FP scheduling list type implements the Fixed Priority (FP) discipline among the tasks assigned to the scheduling list. In the FP discipline, a priority is assigned to each task. Task priority may be modified during runtime. In order to maintain consistency, tasks that are assigned to an FP scheduled list should not be of the infinite-loop type without waiting for event suspension in order to avoid starving lower-priority tasks. Only the lowest-priority task could be implemented as an infinite-loop code.
- Remarks
- GS_LCBType_FP
Main scheduling list related functions #
Creating and initializing a scheduling list #
A scheduling list can easily be created using:
GS_LCB * gu_Get_LCB (enum lcbtype lcbtype)The gu_Get_LCB function creates a new scheduling list and it is defined according the parameter type passed.
The task is created with the following parameters:
lcbtype It is a valid scheduling list type. This parameter defines the scheduling discipline applied over all the tasks assigned to the scheduling list.
- Returns
- The gu_Get_LCB function returns a pointer to the GS_LCB structure associate with the scheduling list created. This pointer should be used in all the references to the scheduling list.
Scheduling list / Processor association #
A processor is associated with a scheduling list with the following function:
G_INT32 gu_LCB_Associate_PCB (GS_LCB * plcb, G_INT32 CPUID, G_INT32 priority )By using the gu_LCB_Associate_PCB function, a system processor can be associated with a scheduling list. Each association has a determined priority. In order of decreasing priority, the processor will search the scheduling lists for the first task ready state.
The processor is associated with the following parameters:
plcb It is a pointer to the GS_LCB of the scheduling list CPUID It is the ID of the processor to be associated with the scheduling list. priority It is the priority for the assignment. Highest priority (lowest value) will be the first scheduling lists looking for the first task in ready state.
- Returns
- The gu_LCB_Associate_PCB function return G_TRUE if successful, G_FALSE otherwise
Task / Scheduling list association #
A task is assigned to a scheduling list with the following function:
G_INT32 gu_SetTaskList (struct gs_tcb * ptcb, struct gs_lcb * plcb )The gu_SetTaskList function assigns a task into a scheduling list. Consequently, the task will be schedule according the priority discipline of the scheduling list.
The task is assigned tothe scheduling list with the following parameters:
ptcb It is a pointer to the GS_TCB structure of the task plcb It is a pointer to the GS_LCB structure of the scheduling list
- Returns
- The gu_SetTaskList function returns G_TRUE if successfull, G_FALSE otherwise



